Quantum X-ray microscope
Posted: 26 Nov 2020, 05:45
Engineers at Brookhaven National Laboratory have designed a strange new X-ray microscope that takes advantage of the world of quantum physics to "ghost image" biomolecules in high resolution but at a lower radiation dose.
X-ray microscopes are useful tools for imaging samples in high resolution, but the radiation involved can damage sensitive samples such as viruses, bacteria and some cells. Reducing the radiation dose is one way around that problem, but that also reduces the resolution of the image.
The Brookhaven team has found a way to maintain higher resolution with a lower radiation dose, using the phenomena of quantum physics.
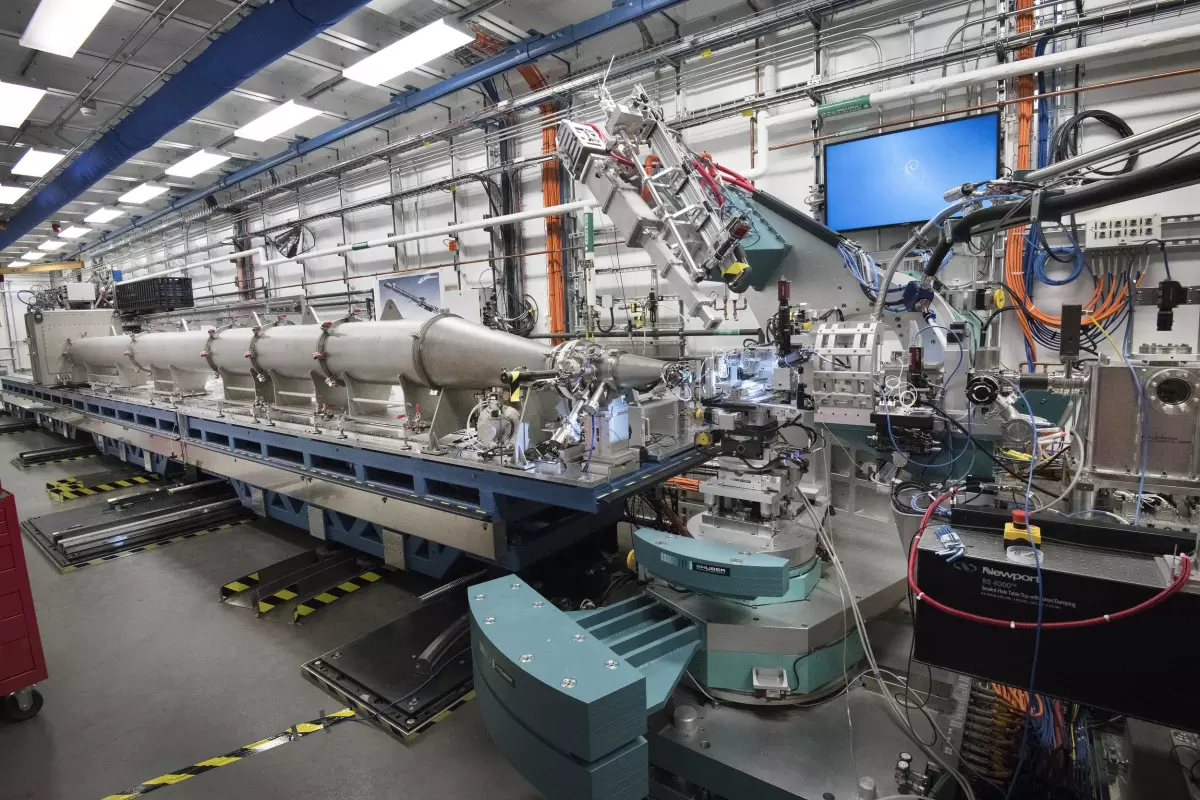
In a standard X-ray microscope, one beam of photons is sent through a sample and collected by a detector on the other side. But in the team’s new quantum-enhanced X-ray microscope, the beam is split into two and only one half passes through the sample – and yet, both beams take measurements.
And it’s all thanks to a strange phenomenon known as quantum entanglement. Essentially, two particles can become so entwined with each other that interacting with one will change the state of its partner instantly, no matter how much distance separates them. That implies information is moving between them faster than the speed of light.
In the case of the new X-ray microscope, the beam splitter produces pairs of entangled photons. One of them passes through the sample, and carries the information to the detector as usual. But at the same time, that causes its partner to automatically change its state too, even though it hasn’t come into contact with the sample. When it then hits its own detector, extra information can be gleaned from it.
The image below shows how the quantum X-ray microscope works – the X-ray beam is split into two. The left beam passes through the sample then hits a detector as normal. The right beam doesn't touch the sample at all, but it still records information due to the phenomenon of quantum entanglement.
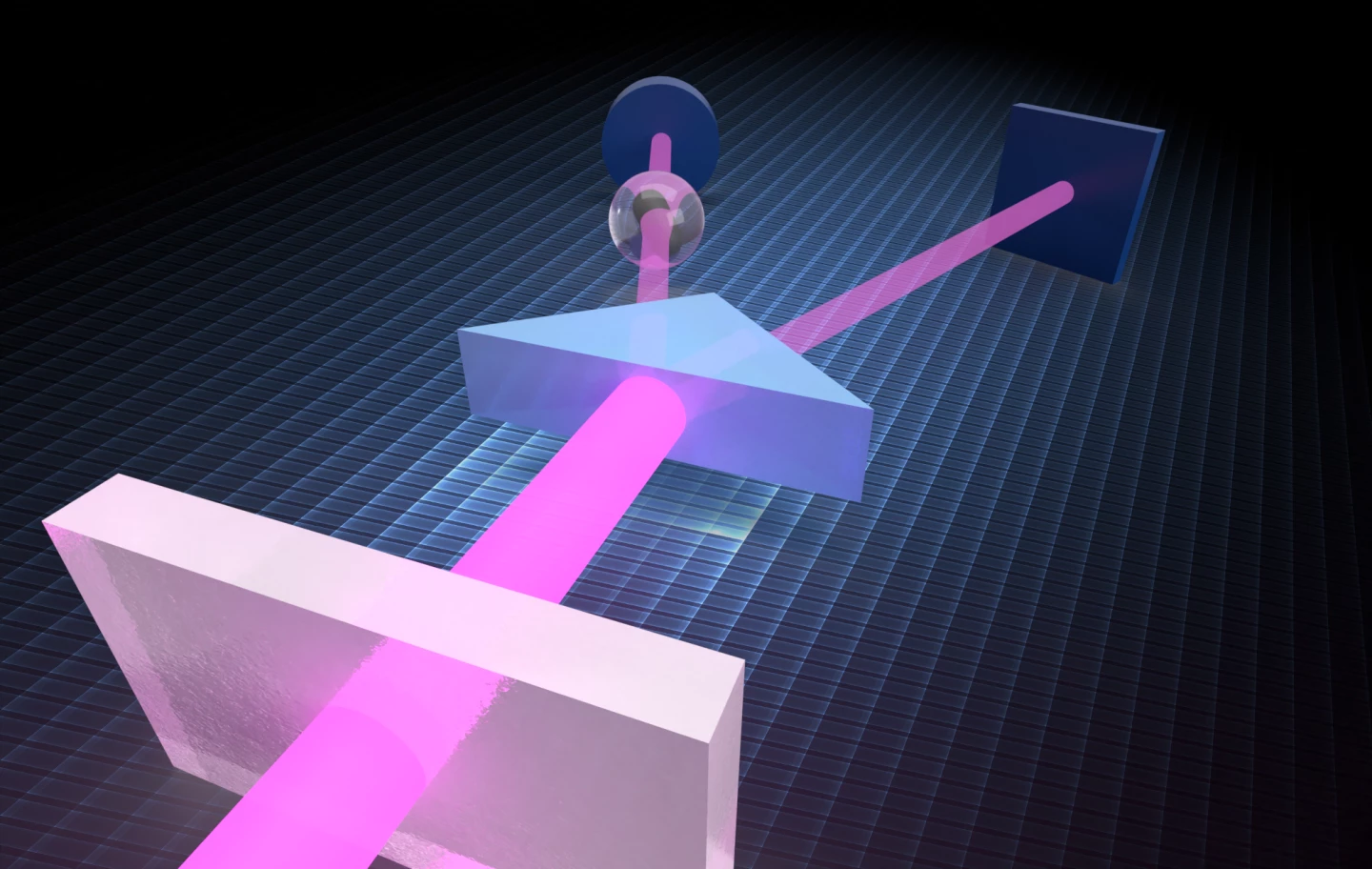
"One stream goes through the sample and is collected by a detector that records the photons with good time resolution, while the other stream of photons encodes the exact direction in which the photons propagate.
It sounds like magic. But with mathematical calculations, we’ll be able to correlate the information from the two beams", says Andrei Fluerasu, a lead beamline scientist on the project.
This process is referred to as "ghost imaging", and so far it’s only been used with photons of visible light. The new microscope would be the first to adapt the technique to X-rays, allowing images to be captured of samples smaller than 10 nanometers, without destroying them.
X-ray microscopes are useful tools for imaging samples in high resolution, but the radiation involved can damage sensitive samples such as viruses, bacteria and some cells. Reducing the radiation dose is one way around that problem, but that also reduces the resolution of the image.
The Brookhaven team has found a way to maintain higher resolution with a lower radiation dose, using the phenomena of quantum physics.

In a standard X-ray microscope, one beam of photons is sent through a sample and collected by a detector on the other side. But in the team’s new quantum-enhanced X-ray microscope, the beam is split into two and only one half passes through the sample – and yet, both beams take measurements.
And it’s all thanks to a strange phenomenon known as quantum entanglement. Essentially, two particles can become so entwined with each other that interacting with one will change the state of its partner instantly, no matter how much distance separates them. That implies information is moving between them faster than the speed of light.
In the case of the new X-ray microscope, the beam splitter produces pairs of entangled photons. One of them passes through the sample, and carries the information to the detector as usual. But at the same time, that causes its partner to automatically change its state too, even though it hasn’t come into contact with the sample. When it then hits its own detector, extra information can be gleaned from it.
The image below shows how the quantum X-ray microscope works – the X-ray beam is split into two. The left beam passes through the sample then hits a detector as normal. The right beam doesn't touch the sample at all, but it still records information due to the phenomenon of quantum entanglement.

"One stream goes through the sample and is collected by a detector that records the photons with good time resolution, while the other stream of photons encodes the exact direction in which the photons propagate.
It sounds like magic. But with mathematical calculations, we’ll be able to correlate the information from the two beams", says Andrei Fluerasu, a lead beamline scientist on the project.
This process is referred to as "ghost imaging", and so far it’s only been used with photons of visible light. The new microscope would be the first to adapt the technique to X-rays, allowing images to be captured of samples smaller than 10 nanometers, without destroying them.